RESEARCH
Organic pillars pre-intercalated V4+-V2O5 center dot 3H(2)O nanocomposites with
School of Physics and Telecommunication Engineering/Achievements 2021-02-16 15:48:38 From:School of Physics and Telecommunication Engineering Hits: Favorite
作者:Yan, HL (Yan, Honglin)[ 1 ] ; Ru, Q (Ru, Qiang)[ 1 ] ; Gao, P (Gao, Ping)[ 1 ] ; Shi, ZL (Shi, Zhenglu)[ 1 ] ; Gao, YQ (Gao, Yuqing)[ 1 ] ; Chen, FM (Chen, Fuming)[ 1 ] ; Ling, FCC (Ling, Francis Chi-Chun)[ 2 ] ; Wei, L (Wei, Li)[ 3 ]
查看 Web of Science ResearcherID 和 ORCID
APPLIED SURFACE SCIENCE
卷:
文献号:
DOI:
出版年:
文献类型:Article
摘要
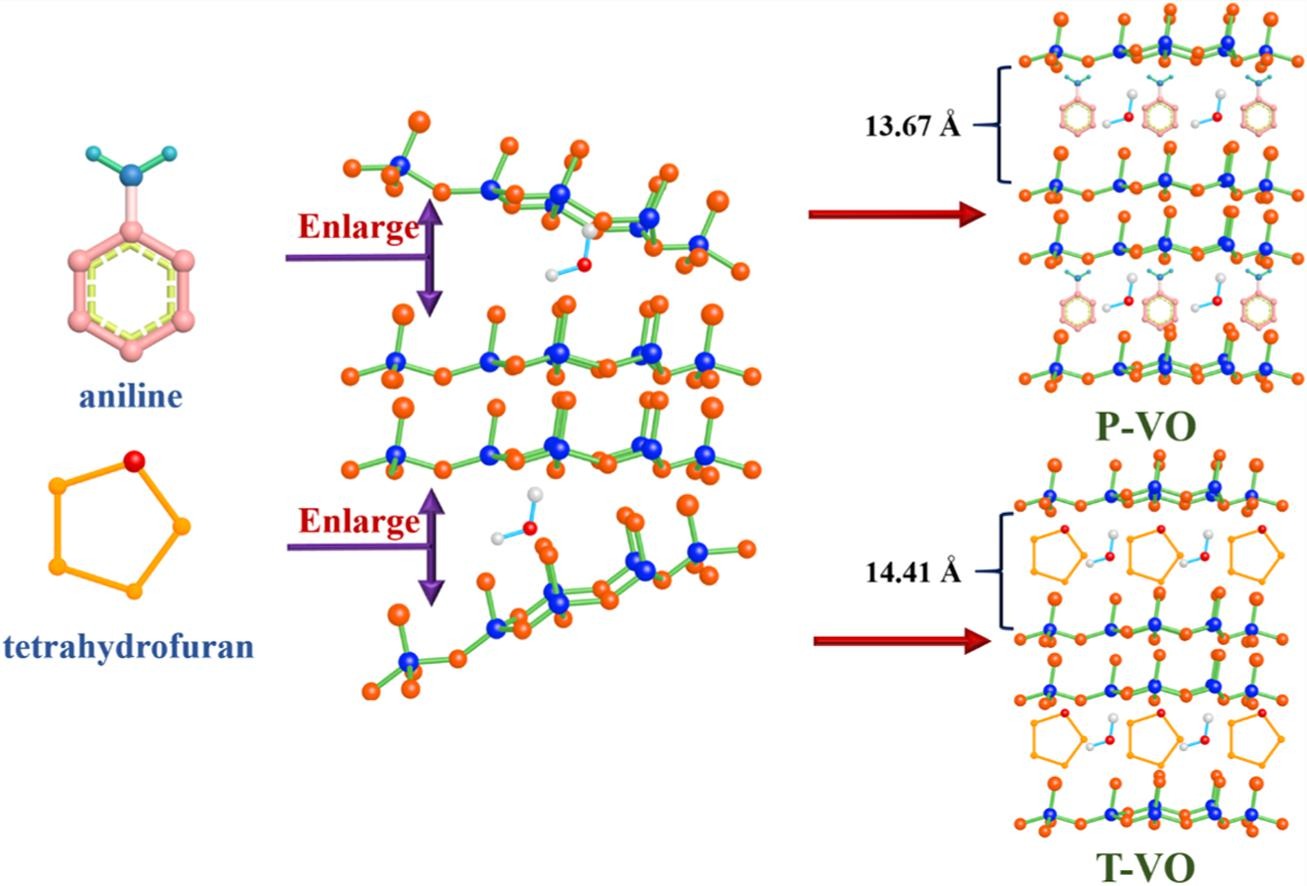
As cathodes for aqueous Zn-ion batteries, the repetitive insertion/extraction and strong polarization of Zn2+ during cycles will severely wreck the structure of layered vanadium oxides, resulting in rapid capacity recession. Hence, the ingenious strategy of PAN/THF-pillars intercalation and V4+/V5+ dual-valence regulation was designed to fabricate PAN or THE pre-intercalated V4+-V2O5 center dot 3H(2)O, denoted as P-VO or T-VO. Owing to the interlayer expansion of organic molecules and the electrochemical reactivity enhancement of mixed V4+/V5+ valence, severe structural collapse of cathodes and strong polarization of Zn2+ can be alleviated. Hence, P-VO and T-VO cathodes can exhibit larger interlayer distances of 13.67 and 14.41 A, more robust construction, faster Zn2+ transmission, and better electrical conductivity. P-VO and T-VO electrodes furnish high zinc storage performance of 251 and 336 mAh g(-1) at 500 mA g(-1), and persistently maintain considerable reversible capacities of 133 and 100 mAh g(-1) after 1000 cycles at a high current density of 10 A g(-1). And the capacitive contribution ratios of P-VO and T-VO can reach up to 75% and 86.4%, respectively. Meanwhile, both two cathodes can endure extreme ambient conditions from -15 degrees C to 45 degrees C. In addition, the insertion mechanism of Zn2+ was also investigated via in-situ XRD and ex-situ XPS.
关键词
作者关键词:Aqueous Zn-ion batteries; Organic PAN/THF pillars; Mixed V4+/V5+valence; In-XRD
KeyWords Plus:CATHODE MATERIAL; PERFORMANCE; BATTERIES
Organic pillars pre-intercalated V4 -V2O5·3H2O nanocomposites with enlarged inte.pdf
