RESEARCH
Low energy consumption flow capacitive deionization with a combination of redox
School of Physics and Telecommunication Engineering/Achievements 2021-02-22 11:29:43 From:School of Physics and Telecommunication Engineering Hits: Favorite
作者:Wei, Q (Wei, Qiang)[ 1 ] ; Hu, YD (Hu, Yudi)[ 1 ] ; Wang, J (Wang, Jian)[ 1 ] ; Ru, Q (Ru, Qiang)[ 1 ] ; Hou, XH (Hou, Xianhua)[ 1,2 ] ; Zhao, LZ (Zhao, Lingzhi)[ 1,2 ] ; Yu, DYW (Yu, Denis Y. W.)[ 3 ] ; San Hui, K (San Hui, Kwan)[ 4 ] ; Yan, DL (Yan, Dongliang)[ 5 ] ; Hui, KN (Hui, Kwun Nam)[ 6 ]
CARBON
卷:
页:
DOI:
出版年:
文献类型:Article
摘要
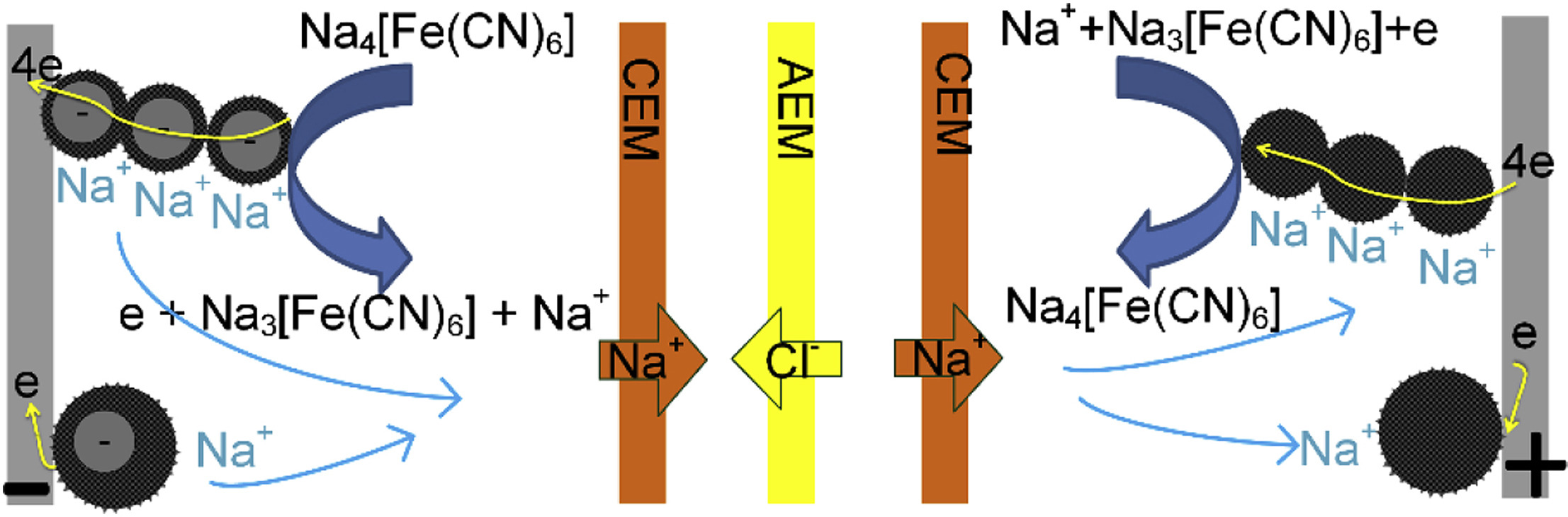
Flow-electrode capacitive deionization (FCDI) is a new sustainable desalination technology where continuous desalination can be achieved by the electrodialysis coupling method. However, its development is hindered owing to high energy consumption and low salt removal rate. Herein, by combining ferri-/ferrocyanide redox couple with flow activated carbon (AC)/carbon black (CB) slurry, continuous desalination process is achieved with a high salt removal rate of 1.31 mg cm(-2) s(-1) and low energy consumption of 102.68 kJ mol(-1) at the current density 2.38 mA cm(-2) (50 mA current for a 21 cm(2) active area). The operating voltage plateau can be reduced to 0.69 V when 10 wt% AC/CB (mass ratio of 9:1) is mixed with 20 mM/20 mM ferri-/ferrocyanide as the flow electrodes, compared with more than 3 V for only carbon flow or redox medium alone. The influences of carbon content and current densities are further investigated to so that the performances can be controlled. This work enables the development of energy-saving desalination systems by coupling FCDI with redox desalination technique. (C) 2020 Elsevier Ltd. All rights reserved.
关键词
作者关键词:Electrochemical desalination; Flow-electrode capacitive deionization; Activated carbon/carbon black; Redox desalination
KeyWords Plus:WATER DESALINATION; PERFORMANCE; ELECTRODE; REMOVAL; SALT